Circular Design Thinking
A methodology for sustainability
Circular Design Thinking is a strategic design methodology aimed at identifying new opportunities for circularity and creating sustainable outcomes.
What is Circular Design Thinking?
Circular Design Thinking is the result of the reworking of various design tools and techniques, combining strategic design and regenerative design into a unique, flexible, and holistic methodology aimed at identifying new opportunities for circularity and creating sustainable outcomes.
The consistent reworking of tools and models from diverse and often disparate design theories allows for a great degree of flexibility and adaptability. It offers a toolkit capable of being applied depending on the specific circumstances of the project.
Thanks to the Circular Design Thinking methodology, it is possible to address the design of products and services, communication strategies, digital marketing, rebranding operations, web design, the creation and launch of sustainable businesses, as well as sustainability and circular economy projects, and much more.

Transform your business into a sustainable operation with HENRY & CO.’s services.
Innovate, communicate, rethink, and design new sustainable activities and business processes using the Circular Design Thinking methodology.
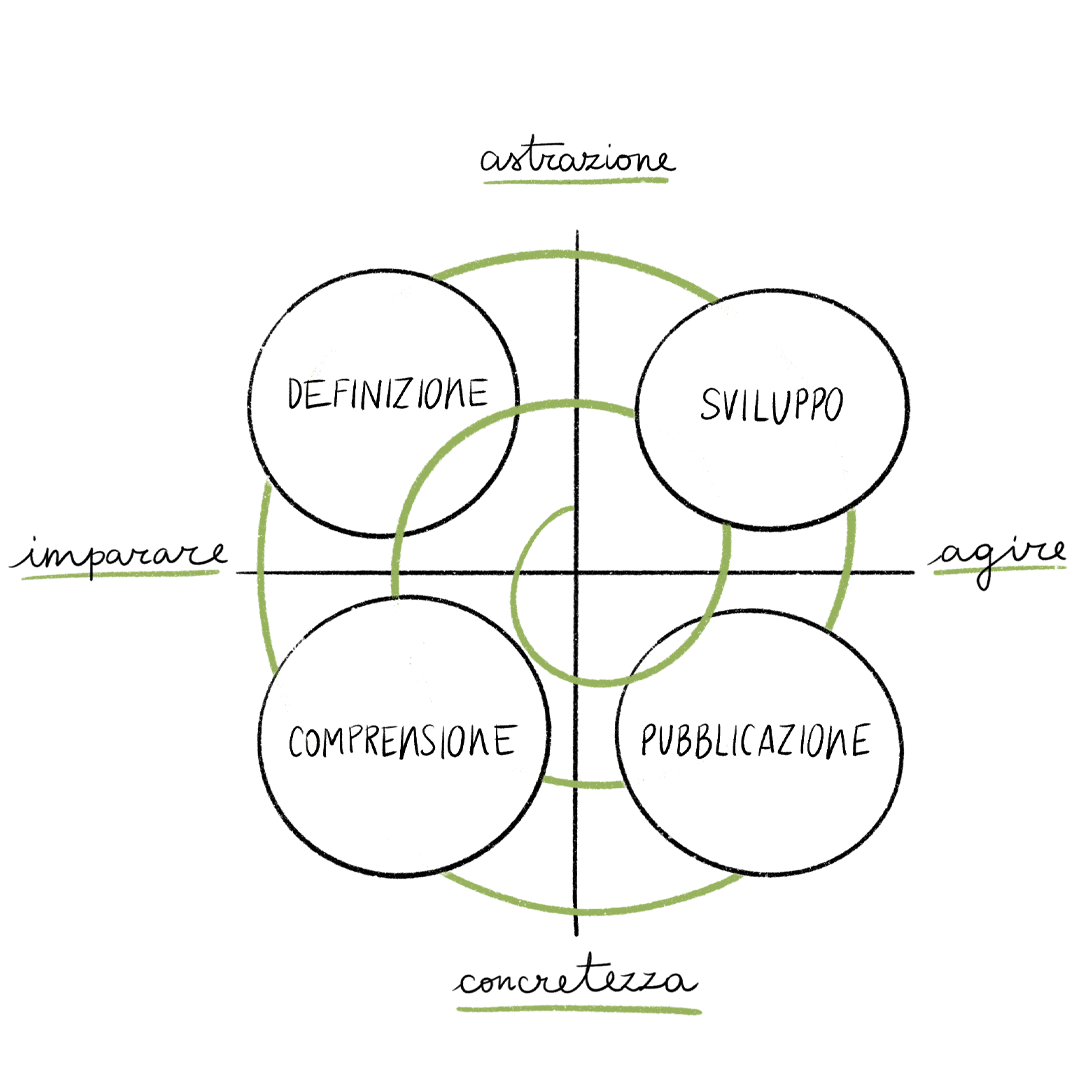
Circular Design Thinking in practice
Circular Design Thinking consists of four phases. Each phase is associated with specific toolsets and exercises: understanding, defining, developing, and publishing.
Despite the apparent linearity of the process, the method naturally involves constant overlap between the phases, oscillating between understanding and definition, development and publication, depending on the project. Therefore, this methodology can be applied at any stage of development and is most effective when implemented from its early stages.
As with any truly effective strategic design, Circular Design Thinking is a co-participatory design methodology that involves key decision-makers in the business processes and includes them in the activities aimed at reaching a unified, shared, and resilient solution.
The phases of Circular Design Thinking
01
Understanding
Explore new scenarios and opportunities that can bring value and sustainability to all stakeholders.
What goals do I intend to pursue? How will I know when I’ve reached them? Who is the main user? What do they need? What do they want? What’s available in the market?
02
Definition
Define goals, KPIs, strategy, and activities necessary to achieve sustainable and innovative results.
How can I stand out from the market? How can I solve my users’ problems and desires? How can I offer a more sustainable solution? How should I structure the project?
03
Development
Develop your solution by solving all identified problems and extending evaluations to the resulting social, economic, and environmental impacts.
How do I resolve my problem? How do I develop my solution? Which solution has the least impact?
04
Publishing
Launch your solution by integrating feedback systems and post-launch evaluations to measure its effectiveness and impact.
Did the solution meet expectations? Was the generated impact reduced? How can I maintain a relationship with the client? How can I stay on the right path?
Why apply Circular Design Thinking?
Circular Design Thinking arises from the ethical and economic need to provide companies with a methodology capable of generating virtuous and sustainable innovation, in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the UN.
Thanks to Circular Design Thinking, it is possible to guide the process of ideation and realization of an innovation project by combining business objectives with social, environmental, and economic interests, to achieve sustainable results in terms of impact and value for stakeholders.

Our goals
SDGs: UN's Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are 17 goals for 2030 agreed upon by the UN as part of the Global Agenda for Sustainable Development.
FAQ
Strategic design is a discipline focused on integrating design into a company’s strategic decision-making process. It goes beyond the aesthetic aspect of design and focuses on creating long-term value, improving competitiveness, and meeting the needs of users and customers.
Strategic design process: Strategic design follows a structured process that consists of several stages. It starts with a thorough analysis of market needs, trends, and competitors. Then, company goals are identified, and a strategic vision is developed. During the ideation stage, innovative solutions are generated that incorporate design as a strategic tool. Finally, the final results are prototyped, tested, and implemented.
Advantages of strategic design:
- Competitive differentiation: Strategic design allows companies to stand out from the competition by offering unique and innovative solutions that effectively meet customer needs.
- Value creation: By integrating design into decision-making, tangible and intangible value is created for the company. Strategic design can contribute to product optimization, enhance the customer experience, and increase overall satisfaction.
- Innovation: Strategic design fosters innovation through the application of design thinking methods and tools. This encourages the emergence of new ideas, approaches, and products that respond to market challenges.
- Customer trust: Investing in strategic design demonstrates a company’s commitment to quality, attention to detail, and user experience. This helps build trust and loyalty toward the brand.
- Operational efficiency: Through strategic design, business processes can be optimized, costs reduced, efficiency improved, and errors minimized.
Strategic design is a powerful methodology that combines design and business strategy to create successful solutions. Investing in strategic design can provide competitive advantages, create value for the company, stimulate innovation, and increase customer trust. Contact strategic design professionals to find out how this discipline can transform your company and lead it to success.
Regenerative Design is an innovative approach that aims to create solutions that not only reduce environmental impact but also regenerate and restore ecosystems. This discipline focuses on designing systems that work in harmony with nature, restoring natural cycles, enhancing resources, and promoting long-term sustainability.
Principles of Regenerative Design:
- Material and energy cycles: Regenerative Design revolves around designing systems that optimize resource use, reduce waste, and promote material recycling and reuse. It seeks to mimic natural cycles to create efficient and sustainable systems.
- Diversity and resilience: Regenerative Design promotes diversity and resilience in designed ecosystems. It aims to create robust and adaptable systems capable of addressing environmental and social challenges, ensuring sustainability over time.
- Interconnection: Regenerative Design takes into account the relationships and interconnections between the elements of a system. Its goal is to create systems that foster collaboration among stakeholders, promoting resource-sharing and synergy.
Benefits of Regenerative Design:
- Environmental regeneration: Regenerative Design offers the opportunity to restore damaged ecosystems, improving air, water, and soil quality. This contributes to biodiversity conservation and ecosystem balance.
- Long-term sustainability: Through Regenerative Design, sustainable solutions can be created that meet present needs without compromising future generations. It promotes efficient resource use, waste reduction, and environmental conservation.
- Resilience to global challenges: Regenerative Design helps tackle environmental and social challenges, such as climate change, resource scarcity, and biodiversity loss. By promoting resilience, we can better address such challenges and build a sustainable future.
- Economic benefits: Regenerative Design can yield economic benefits, such as reduced energy costs, increased process efficiency, and attracting new markets and customers sensitive to sustainability.
Design Thinking is a problem-solving methodology that emphasizes a user-centered approach to tackling complex issues innovatively and creatively. This approach serves to identify effective solutions tailored to users’ needs. Design Thinking is widely used across various sectors, including industrial design, business innovation, education, and more. Its main purpose is to solve problems, improve existing products or services, and develop new ideas. This methodology relies on a deep understanding of users’ needs and desires, encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration and continuous iteration for optimal results.
For more information on Design Thinking and how it can be applied, you can refer to this detailed article on Design Thinking.
Design Thinking was not created by a single person, but evolved over time through the contributions of many individuals and organizations. However, its dissemination and systematization can be attributed to several key sources:
- IDEO: IDEO, a renowned design and innovation consultancy, was one of the first to adopt and promote Design Thinking in the 1990s. IDEO contributed significantly to the development of the stages and processes of Design Thinking.
- David Kelley: David Kelley, founder of IDEO, played a pivotal role in promoting Design Thinking. He has dedicated his career to spreading this methodology and has taught Design Thinking at Stanford University.
- Tim Brown: Tim Brown, CEO of IDEO, has written extensively on the subject and contributed to making Design Thinking accessible to a broader audience through books and lectures.
Thus, there isn’t a single creator of Design Thinking, but rather a community of innovators who developed and spread this methodology.
If you want to learn more about the evolution and origin of Design Thinking, you can read this historical article.
Design Thinking employs a variety of tools and techniques that help guide the problem-solving and innovation process. Some classic tools of Design Thinking include:
- Brainstorming: A creative idea-generation technique in which a group of people offers ideas in a non-critical, free-flowing manner.
- Personas: Creating imaginary user profiles to better understand their needs, desires, and behaviors.
- Journey Mapping: A visual representation of the path a user takes through a product or service, highlighting critical touchpoints.
- Prototyping: Building experimental versions of a product or service to test and quickly refine ideas in a cost-effective way.
- User Testing: Verifying solutions with end users to gather real feedback and identify any necessary improvements or issues.
These are just some of the common tools used in Design Thinking. However, it is important to note that the methodology is highly flexible and can incorporate a wide range of techniques depending on the project’s specific needs. You can find more information about the tools of Design Thinking in this detailed article.
